Ever wondered when you type a url in the address bar of a browser, how does the browser knows which page to display ?
If you've visited that website before, its understandable that the website address is saved in cache but what for the websites you're visiting for the first time. Don't know?? The answer is quite simple. DNS
The Domain Name System or as people call it DNS is by far the most important and over-looked parts of the internet. Without DNS there is nothing called internet. We would all be licking stamps to pay our bills, driving to an actual store to purchase something, reading the newspaper to see what movies were showing, or visiting the video store each week to rent new movies and music.
How DNS comes into play ?
We are already aware that computers that make up the internet are set up in large networks that communicate with each other via underground or under water wires and are identified using strings known as IP addresses.
Since it is nearly impossible for us to retain all those millions of IP addresses, DNS is used to translate actual names(URLs) into these numbers.
DNS working ...
Let's start with you typing your favorite website url in the browser, mine being netflix.com. Now, when we type www.netflix.com in the address bar, we'll actually be looking for www.netflix.com., Yes, there is a dot at the end of the domain name. Even though we never typed it, it is still there. Seems a bit odd though. Stay with me for a few more minutes and you'll get it all.
So, where was I.. The end dot represents the root of the internet's name space. When you first search for www.netflix.com., your browser and operating system would first check if they know what the IP address already is. It could be configured on the computer or could be in the memory (as we often call it CACHE). If the IP address is already configured, well and good, but what if neither the browser nor the operating system know the IP address. IS THIS THE END ?
What happens NOW ?? 🤔🤔
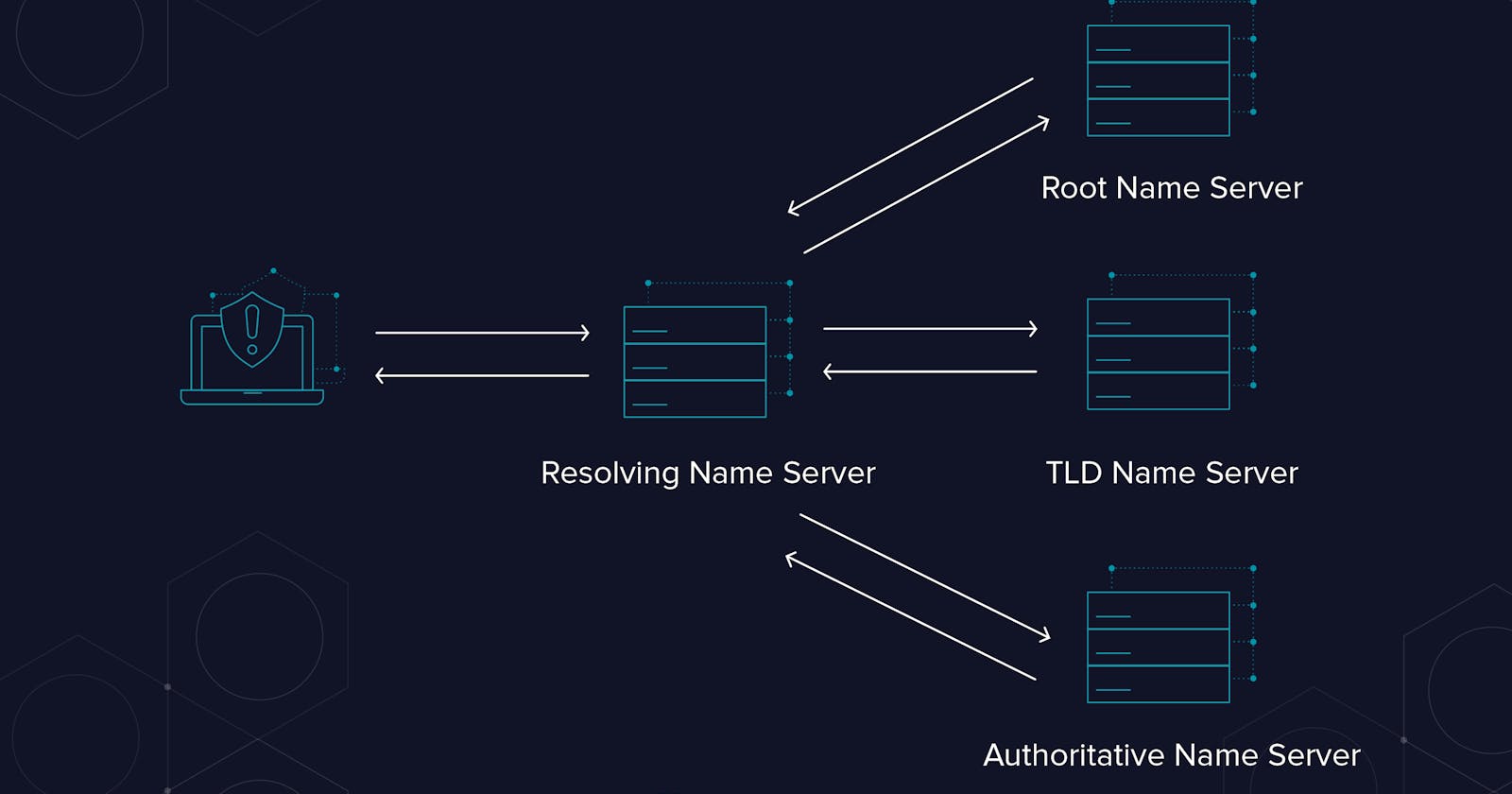
The operating system is configured to ask a resolving name server, for the IP addresses it does not know about. This resolving name server is the workhouse of the DNS lookup. It can be configured manually or automatically within the operating system. Your operating system asks the resolving name server for www.netflix.com., the resolving name server may or may not have this in memory.
The only thing that all resolving name servers should be aware of, is where to find the root name servers. Yes, that dot at the end of domain name.
Now this root name server will guide where to find the com name servers.
The COM name servers are called Top Level Domain Name Servers or TLD name servers. The resolving name server then take all of this information from the root name server, put it in its cache, and then goes directly to the COM TLD name servers. When the resolving name server queries www.netflix.com, the TLD name server responds where to find the ''netflix.com'' name servers. This next set of name servers are authoritative name servers.
Proceeding ahead, the resolving name servers take the response from TLD name servers , stores it in cache and queries netflix.com name servers.
At this point the authoritative name server will respond by telling the resolving name server that The IP address you've been looking for is 192.173.64.0/18. The resolving name server takes this information, stores it in the cache, gives the reply to operating system. The operating system then gives this IP address to the browser, the browser then makes a connection to the IP address requesting the web page for www.netflix.com.
The whole process might seem a bit complex, which in no-doubt it is, but this entire cycle takes less than a blink of an eye to complete.
Pretty cool... Isn't it !!